Restoration
Treatments
Dental Composite (formerly Amalgam/Filling)
A small filling that repairs a tooth after decay or a fracture.
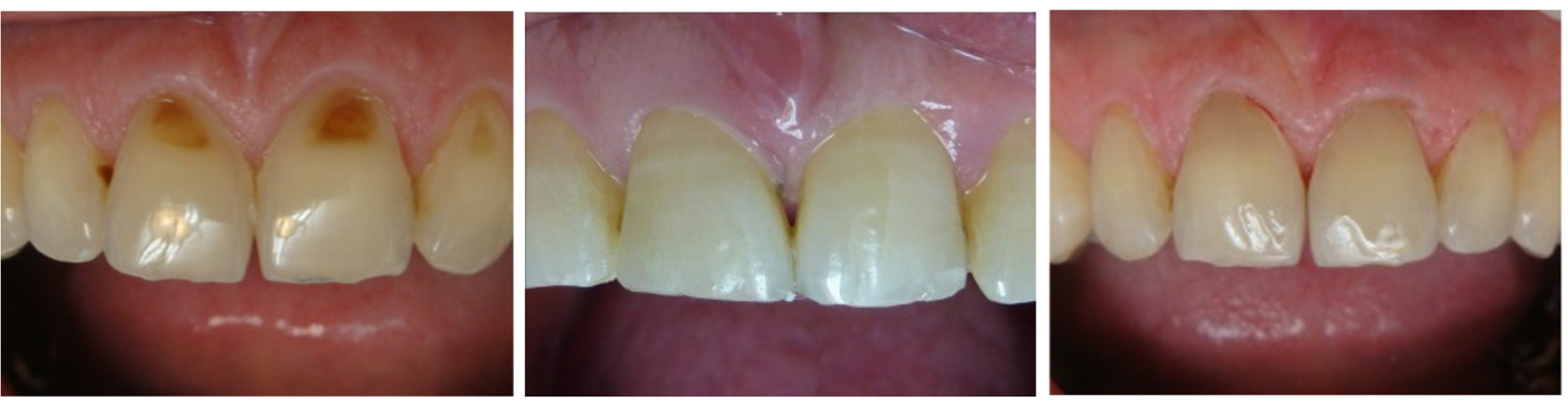
Inlay
A small, indirect restoration made of composite, ceramic, or gold, crafted by a dental technician to restore a damaged tooth.

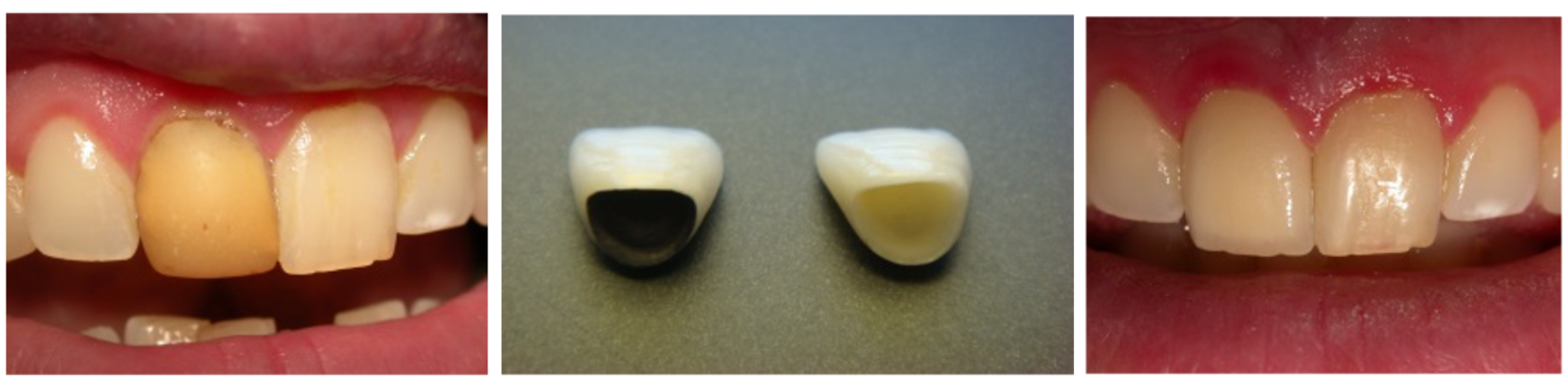
Dental Crown
A replacement structure made of ceramic and zirconium, used in cases of severe decay or root treatment. The crown covers the entire tooth, providing protection.
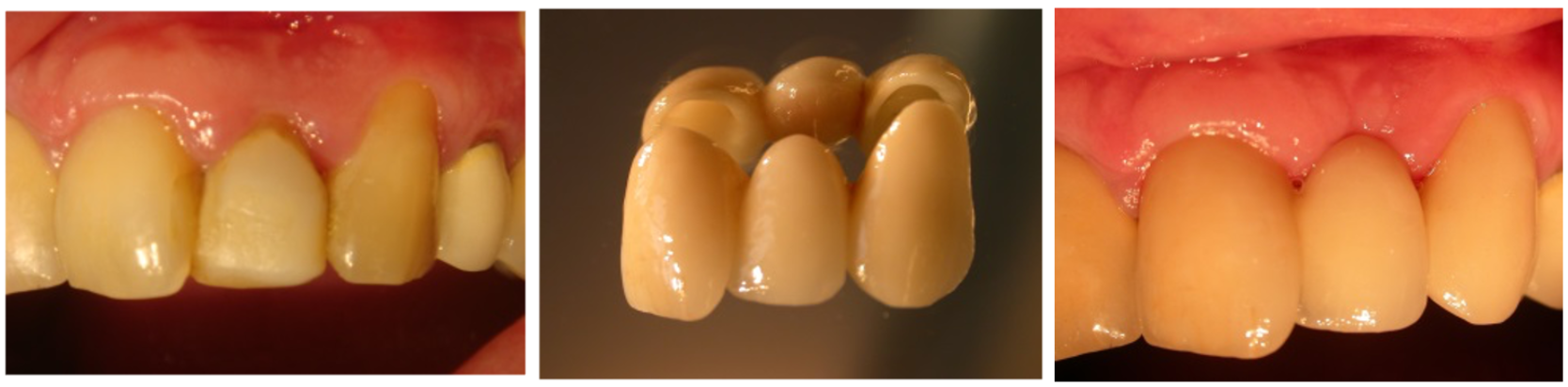
Bridge
A fixed ceramic prosthesis, bonded to adjacent teeth. The bridge replaces one or more missing teeth, serving as an alternative to dental implants. It is fixed in the mouth and cannot be removed.
Comprehensive Guide to Restoration
Conservative Treatments
Dental Composite (formerly Amalgam/Filling)
A small filling used to repair a tooth after decay or a fracture.
Inlay
A small, indirect restoration made of composite, ceramic, or gold, crafted by a dental technician to restore a damaged tooth.
Crown
A dental crown is a restoration made of ceramic, metal, or composite that fully covers a damaged or worn tooth, providing a durable restoration of its shape, function, and aesthetics.
Bridge
A dental bridge is a fixed prosthesis that replaces one or more missing teeth. It is supported by adjacent teeth, which serve as anchors for securing the intermediate artificial teeth, ensuring natural functionality and appearance.
When to Consider a Dental Restoration?
You should consider a dental restoration if you experience any of the following conditions:
Damaged Teeth: To repair fractures or chips that affect function and appearance.
Tooth Decay: When cavities require a filling or crown to protect the tooth.
Worn Teeth: To address wear from aging, bruxism, or other factors, restoring the shape and function of the teeth.
Aesthetic Reasons: Enhancing the appearance of your teeth.
What Materials Do We Use for Dental Restorations?
- Ceramic
- Composite
- Metal
- Porcelain
- Resin Composite
- Zirconia
- Gold













